FA:Factory Automation
Factory automation (FA) refers to automation in factories.
FA often targets the fields of machining, assembly, material handling, and inspection, The main objectives are to reduce costs, stabilize quality, ensure worker safety, improve CT, and manufacture products that cannot be made by hand.
Automation is essential for production activities in factories,
Sakae offers the best solutions for our customers based on the experience of our dedicated staff and our many years of experience in automation.
%20(1).jpg?width=1930&height=1120&name=FA%E8%87%AA%E5%8B%95%E5%8C%96%E3%80%80%E8%A1%A8%E9%A1%8C%E9%83%A8%E3%82%A4%E3%83%A1%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B8%E3%83%87%E3%83%BC%E3%82%BF%20(1)%20(1).jpg)
FA & Automation Case Studies
Click on an item for more information.
1. Automated Conveyance:Marking and pin press fitting machine
Marking and pin press fitting machine is a device that performs model engraving and pin press fitting on C/Bs.
It will have a maximum of 14 press-in runs on all six surfaces.
It is a combined machine with upper and lower press-in shafts, a turntable on the side and multiple press-in punches in the rear.
The multiple punches are moved to the press-in position by a 2-axis servo mechanism.
Press fitting is performed by a servo press from behind the moved punch.
The outer case of the device and the turntable are as strong as those of the processing machine because of the rigidity required.

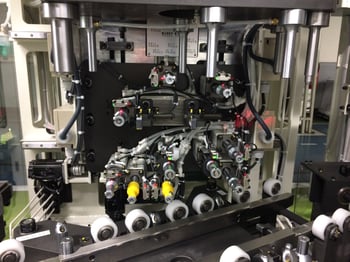
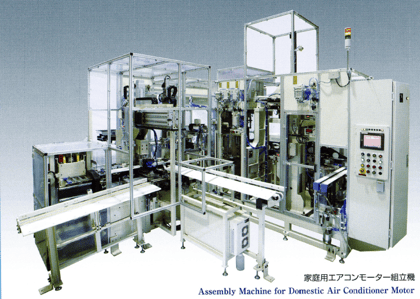
2. Assembly Automation:Motor Assembly Facility
It is a facility that assembles motors for air conditioners.
There are 17st from input to payout, and 7 parts are assembled.
Rotor materials are fed in, magnetized with high voltage, bearing press-fitted onto the shaft, greased, washers inserted, set into the body, and cover press-fitted. The press-fit section includes a variety of content, such as height measurement.
The entire process can be completed within a short cycle time of 13sec.

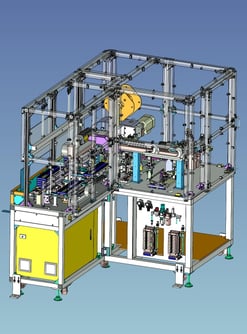
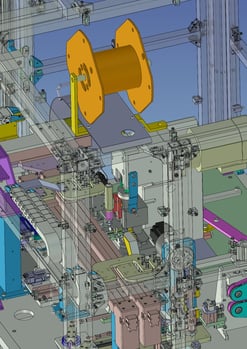
3. Processing Automation:Wire peeling and caulking Machine
It is a machine that performs everything from stripping the outer coating of wire material to caulking the terminals.
Cycle time = 6.5sec
In a very fast cycle time, two wires are stripped of their clothing, caulked and paid out.
After crimping, they are aligned on the discharge pallet.
4. Processing Automation:Motor core heating Machine
It is a machine that heats the motor core (iron core) before resin molding.
By changing the process of raising the temperature with a hot-air furnace to an electric heater, we are contributing to savings in electricity usage.
The heating furnace is a few other units of 4 products x 5 units.
The heating jig is in open/closed contact with the product to eliminate variations in heat conduction and stabilize product temperature.
This eliminates variations in heat conduction and stabilizes product temperature.
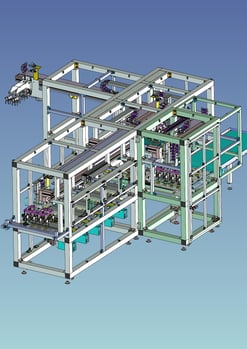
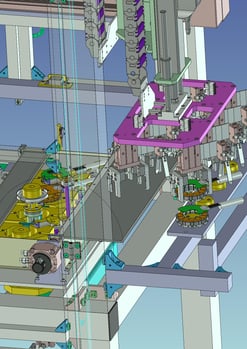
5. Processing Automation:Substrate Cutting Machine
It is a machine that cuts substrates using an air spindle (40,000 rpm) and a φ0.8 end mill.
A feature of this machine is that it is designed to accommodate multiple types of products by replacing jigs.
The servo-driven drive unit makes the contact area of the endmill variable, thereby extending the service life of the endmill,
This leads to a reduction of tool cost by replacing the cutting tool and man-hours required for replacing the cutting tool, thereby reducing man-hours required for replacing the cutting tool.
Chips generated by machining are prevented from scattering by suction from the bottom of the jig, and a mechanism is provided to automatically discharge them together with the cut end material.


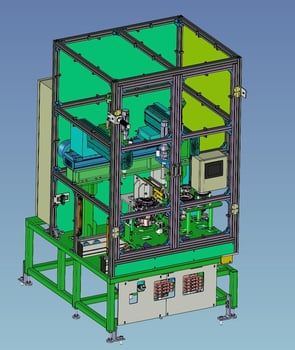
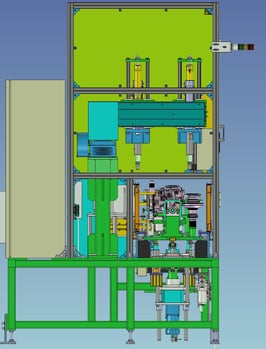
6. Assembly Automation:Screw tightening automation (2-axis screw tightening machine)
It is a machine that tightens the cover bolts of the gear unit.
Tighten the bolt set in the default position with a nutrunner.
Bolts are supplied by pressure feed from the parts feeder, and servo-driven nut runners are used for screw tightening at two locations to support traceability of screw tightening torque values.
In addition, a straight-line robot is used to position the nutrunner, making it compatible with other models.
7. Automated Conveyance:High-frequency nut welding machine
It is a machine that welds a nut heated by high frequency to a plastic part.
Resin parts are fed on special pallets.
Since there are a wide variety of products, workpieces are identified by a camera and fed into the welding process. Nuts are supplied by a parts feeder and heated to 300°C by a high-frequency heating machine. The heated nut is pressed against the resin workpiece to melt the resin and press-fit it.


8. Automated Conveyance:Magnetizing Motor Conveyor
It is a conveyor for loading and unloading motor parts into and out of a magnetizing machine.
Since the products after magnetization have strong magnetism, nonmagnetic materials are used for the parts near the products.
Since the front and back sides of the product need to be converted for loading and unloading, a reversing unit is used.
The reversing unit is also made of non-magnetic material to prevent problems caused by magnetic force.
The outgoing conveyor is equipped with a magnetic force sensor to check magnetization and a camera to read the QR code of the product in order to manage the delivery history.
A camera is used to read the QR code of the product in order to manage the delivery history.
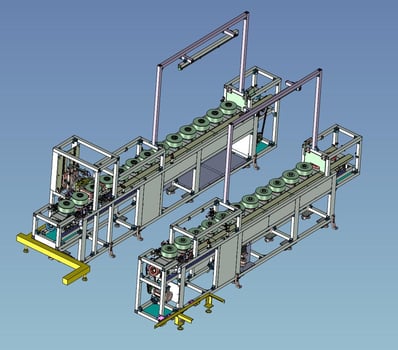
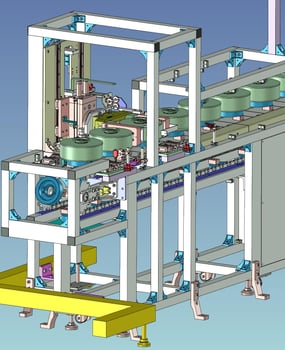
9. Automated inspections:Aluminum casting borehole inspection machine
It is a cesspool inspection machine that uses a laser beam to inspect the inside diameter of a hole.
It irradiates a laser beam of Φ0.2 and detects holes by the amount and direction of reflected light. Since inspections for pits and scratches are becoming more stringent for aluminum castings, this system has made it possible to save manpower by quantitatively quantifying inspections that used to be done visually.


10. Automated Conveyance: Glass substrate supply machine
It is a machine that feeds glass substrates stacked in multiple layers on resin trays into a washing machine, which returns the discharged substrates to the trays and stacks them in multiple layers.
Each substrate is transported in 7 seconds. To prevent scratches and stains on the substrates, the conveyance rollers after removing the substrates are made of resin and are designed to be point-contact.



11. Packaging Automation:Pharmaceutical tablet packaging line
It measures the weight of tablets discharged from the image inspection machine and performs constant packaging. An automatic scale set under the conveyor is used to count the number of pills A stop valve is provided to prevent box-to-box variation due to the extremely light unit weight.
The stop valve opens and closes with a silicon valve to reduce damage to the tablets.



12. Processing Automation:Motor end wire cut out machine
It is a machine that cuts and removes excess copper wire from motor coils. The copper wire is cut with air nippers.
A lot of know-how is packed in the claw that chucks the end wires to prevent the motor core from being lifted up when the end wires are removed after cutting.




13. Assembly Automation:Rubber stopper insertion machine
It is a machine that inserts waterproof rubber plugs into plastic connectors.
Connectors are removed from the table of the supply unit by a robot with a camera to handle a wide variety of products.
Normally, multiple parts feeders for connectors are provided, but by using a single supply unit and a robot with a camera, the system saves space, eliminates setups, and further reduces costs.
Rubber plugs are fed from the parts feeder and inserted into connectors on the index.
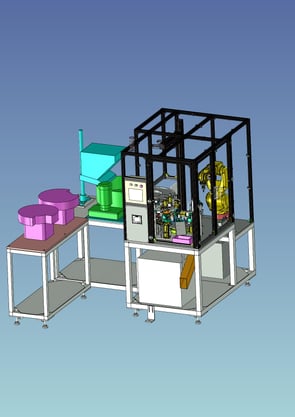
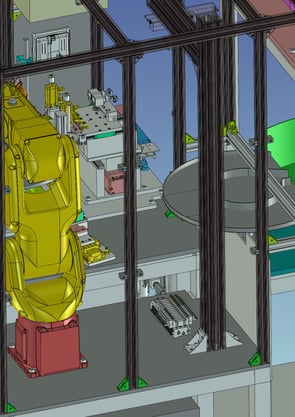
14. Measurement Automation:Inside diameter measurement rank stratification machine
It is a machine that measures the inside diameter of cup-shaped workpieces, ranks the measurement results, and dispenses them by rank.
Cycle time: 40 sec.
Cups placed at an arbitrary angle are taken out by a robot, angle-corrected by a camera, and fed into a measuring jig.
The cup is measured using a Keyence GT sensor and dispensed to the take-out table according to measurement accuracy.
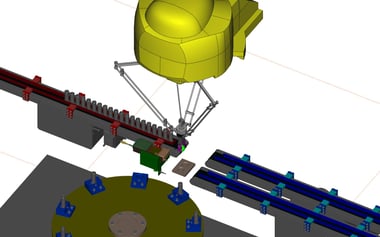
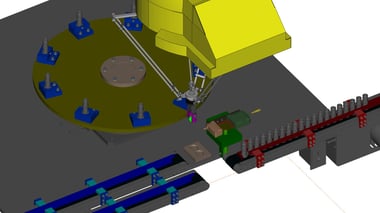
15. Transport Automation:High-speed supply to index (GENKOTSU Robot)
It is a system that uses a prototype robot to supply to an index that is performing high-speed inspection.
Cycle time: 5.0sec/piece
Conventionally, workers performed supply and retrieval by two-handed operation.
The SCARA robot could not keep up with the cycle time, and automation was not possible.
With the adoption of the GENKOTSU robot, we were able to clear the cycle time and automate the process.
Furthermore, by retrofitting the existing indexing machine with a supply and discharge conveyor and robot for automation, a cost-saving introduction was realized.
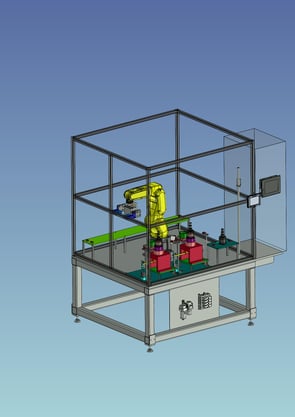
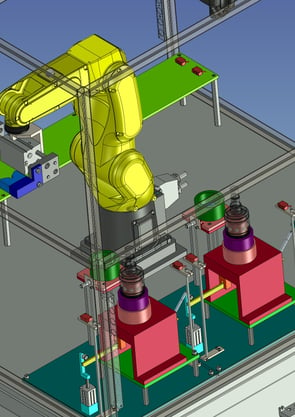
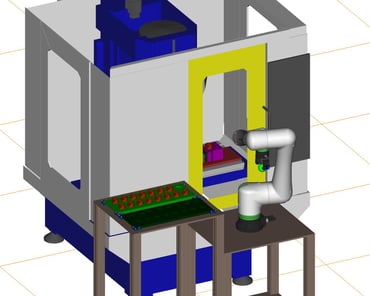
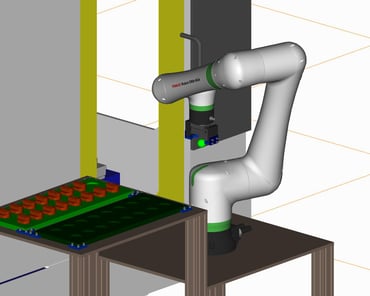
16. Processing Automation:Collaborative robotic processing machine/loading machine saves manpower
It is a machine that uses a cooperative robot to load and unload materials from a processing machine.
The introduction of the robot has made it possible to semi-automate a process that used to require a worker's constant attention due to the small quantity and variety of products. Misalignment due to jig loading, setup changes, etc. and teaching corrections can be easily corrected by using direct teaching, which is a feature of cooperative robots.
This is an example of how a cooperative robot can be easily introduced simply by building a product storage area.
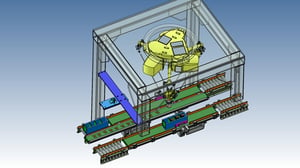
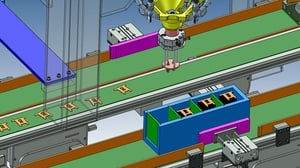
17. Transport Automation:High-speed loading machine for pressed sheet metal (GENKOTSU Robot)
In the past, due to high-mix production and high press discharge speed, workers stacked and packed the products, which could not be automated.
Discharge speed from press: 90 spm
By using a parallel link robot, it became possible to keep up with the cycle time, which had been given up until now. The use of suction to discharge at a fixed position also helps prevent damage to the workpiece.
In addition, the use of parallel link robots has made it possible to install the machine in a smaller space than with multiple SCARA robots.
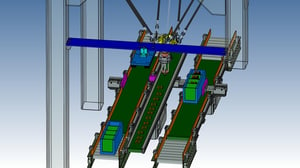
18. Automated inspections:Disk SET Confirmation Machine
FANUC cooperative robot CRX-10IA/L was used to automate the manual process.
Previously, a single operator was working at all times, but with the introduction of the robot, we were able to automate the parts of the process other than workpiece supply.
This machine alternately stacks two types of discs on the jig. After stacking, the robot presses the start button, and the existing sensor makes an OK/NG judgment. The robot's hand camera recognizes the OK/NG result displayed on the touch panel.
The ejection trestle is recognized by the robot's hand camera to compensate for any misalignment in positioning by the operator.
.jpg?width=300&height=169&name=%E3%83%87%E3%82%A3%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AFSET%E7%A2%BA%E8%AA%8D%E6%A9%9F_1%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?width=300&height=169&name=%E3%83%87%E3%82%A3%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AFSET%E7%A2%BA%E8%AA%8D%E6%A9%9F_2%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?width=300&height=169&name=%E3%83%87%E3%82%A3%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AFSET%E7%A2%BA%E8%AA%8D%E6%A9%9F_3%20(1).jpg)
19. Processing Automation:Tap processing robot system
It is a system for drilling and tapping shaft end faces.
The system is now an automatic line with Robodrill and robot interlocked. The robot takes the workpiece from the feeder,
The robot takes the workpiece from the feeder and attaches it directly to the machining jig. The robot uses a double chuck to shorten the time required for mounting and dismounting.
A camera is also incorporated to inspect for the presence or absence of taps and chips after machining.
.jpg?width=300&height=169&name=%E3%82%BF%E3%83%83%E3%83%97%E5%8A%A0%E5%B7%A5%E3%83%AD%E3%83%9C%E3%83%83%E3%83%88%E3%82%B7%E3%82%B9%E3%83%86%E3%83%A0_1%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?width=300&height=169&name=%E3%82%BF%E3%83%83%E3%83%97%E5%8A%A0%E5%B7%A5%E3%83%AD%E3%83%9C%E3%83%83%E3%83%88%E3%82%B7%E3%82%B9%E3%83%86%E3%83%A0_2%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?width=300&height=169&name=%E3%82%BF%E3%83%83%E3%83%97%E5%8A%A0%E5%B7%A5%E3%83%AD%E3%83%9C%E3%83%83%E3%83%88%E3%82%B7%E3%82%B9%E3%83%86%E3%83%A0_4%20(1).jpg)
20. Processing Automation:Tube fusing machine
It is a machine that thermally fuses plastic tubing to specified dimensions.
Tubes are clamped at the top and bottom by a belt feed machine to prevent dimensional deviations due to slippage or misalignment.
A servo motor is used to drive the feeder, allowing the length to be specified in 0.1 mm increments.
Cutting is performed using an electrically heated wire to cut the end face and prevent fraying by fusing the cut surface at the same time.

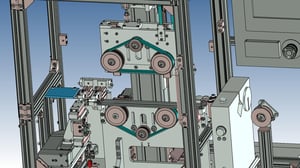
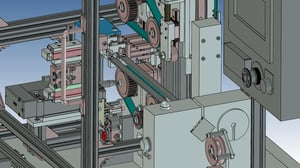
21. Automated Inspections:Visual inspection machine for display monitors
It is a machine that inspects the shape of laser welds on terminals. The shape and size of the laser weld are determined by the image.
Since there are 60 inspection points, one camera is used to inspect two points.
The cycle time is reduced by moving the camera as it takes images.

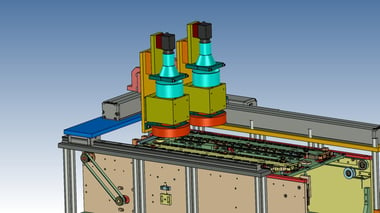
22. Automated Inspections:Visual inspection machine for display monitors
It is a visual inspection machine for electrical control display monitors.
What was previously a combination of stand-alone machines has been successfully automated through the use of robots.
By incorporating robotic transfer, the inspection time and transfer time are offset, resulting in a shorter cycle time.
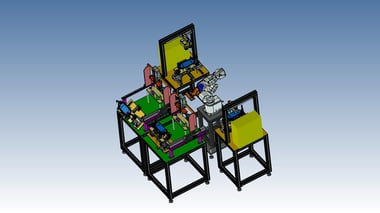
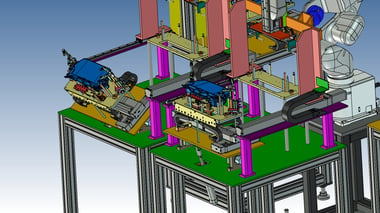
23. Assembly Automation:Screw tightening machine for electrical plastic boxes
This is a machine that tightens screws for mounting the inner plate of a resin box for electrical components.
Previously, screws were tightened by a worker, but this machine is connected to the outlet of the molding machine to achieve automation.
This single machine reduces the workload of one screw-tightening operator (only the supply of the inner plate remains).
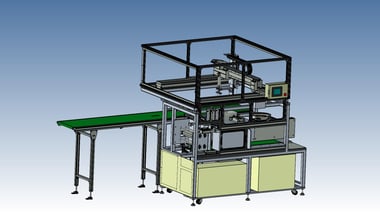
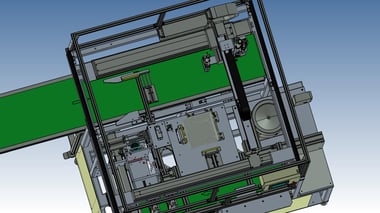
24. Transport Automation:Nut welding machine
It is a machine that performs resistance welding of square nuts to pressed products.
The incorporation of robot transport has made it possible to produce a wide variety of products in small lots with fewer setups.
In addition, the welding jig is no longer needed, and the setup and changeover time for the welding jig has been reduced (3 minutes per day x 20 minutes = 60 minutes).
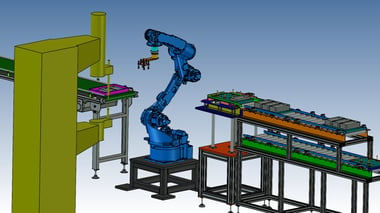
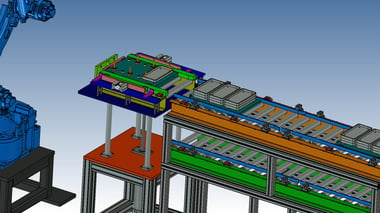
Other examples of dedicated machines
%20(1).jpg) Axis wrapping Machine
Axis wrapping Machine%20(1).jpg) Shaft Dimension Measuring Machine
Shaft Dimension Measuring Machine%20(1).jpg) Cleaning Machine
Cleaning Machine%20(1).jpg) Thermal wax transfer printer
Thermal wax transfer printer%20(1).jpg) Heat Insert Machine
Heat Insert Machine%20(1).jpg) Processing tool
Processing tool

%20(1).jpg)
